
What is the Knowledge Graph?
Knowledge Graph is a database used by search engines to connect different pieces of information and understand the relationships between them. It helps search engines to provide more accurate and relevant search results. Its importance lies in providing users with quick and informative answers, improving search results, and enhancing user experience.
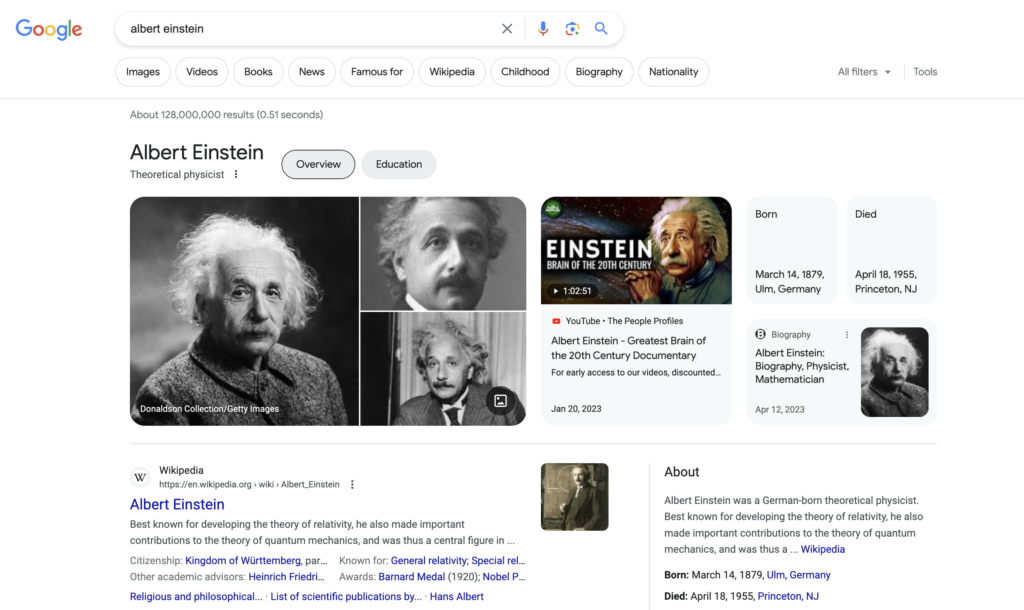
Structured Data
Structured Data is a standardized format used to organize and display information on web pages. It helps search engines to understand the content of a page better and display relevant information in search results. Its importance lies in improving the visibility of a website in search results, increasing click-through rates, and providing richer search results to users. This is the data that you markup to notify Google about the different concepts your website talks about. It’s your entry point into the Knowledge Graph.
Knowledge Graph vs. Structured Data
Structured Data markup can be used to provide structured information to search engines, allowing them to create a Knowledge Graph. By implementing structured data on your website, you increase the likelihood of your website appearing in the Knowledge Graph, thus increasing its visibility. The use of structured data not only helps search engines to understand and categorize your content but also ensures that your content is presented more prominently in search results.
By understanding the connection between Knowledge Graph and Structured Data, website owners can leverage these tools to improve their online presence. Implementing structured data markup and optimizing it for relevant search queries can significantly impact website visibility and click-through rates. Ultimately, the combination of Knowledge Graph and Structured Data can enhance user experience, providing users with accurate and informative search results. Take advantage of these tools, and boost your website’s rankings and visibility on search engines.
Evolution of Knowledge Graph
In recent years, search engines have evolved in their ability to understand and present information to users. The emergence of the Knowledge Graph has revolutionized how search engines like Google organize and display information. The Knowledge Graph is a database that stores vast amounts of information about various topics, people, places, and things.
How Search Engines use Knowledge Graph
Search engines like Google use the Knowledge Graph to improve search results and provide more relevant information to users. By understanding the relationships between different entities and the context in which they exist, search engines can generate more accurate search results. Knowledge Graph helps search engines understand specific queries, enabling them to fulfill user intentions more effectively.
Examples of Knowledge Graph in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs)
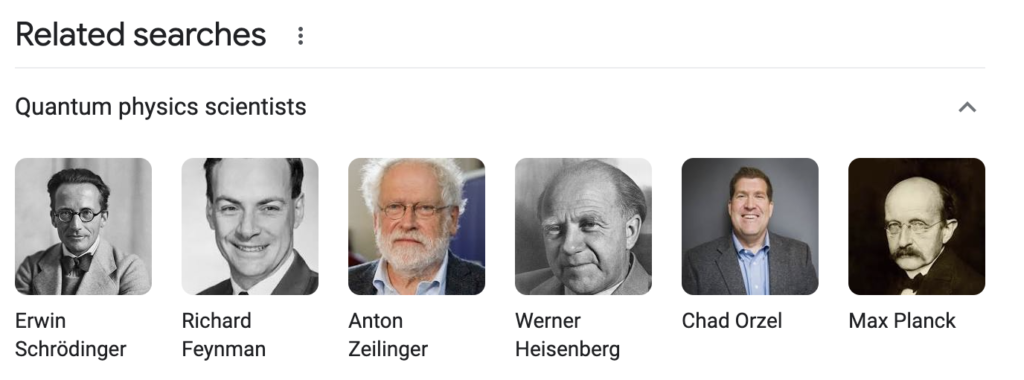
When you search for a famous person, a Knowledge Graph panel appears on the right side of the search results page, showing relevant information about that person. Similarly, when you search for a specific place, the Knowledge Graph panel provides a summary of the location’s details, including maps, photos, and reviews. Knowledge Graph is also used in other search features like “People also ask” and “Related searches,” providing users with additional information and relevant search suggestions.
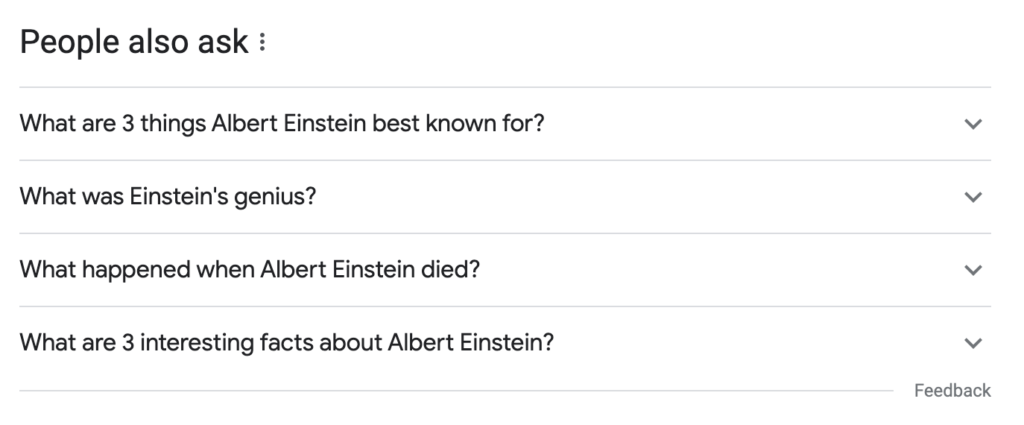
Components of a Knowledge Graph
1. Entities
Entities are the specific topics, people, places, or things that the Knowledge Graph stores information about. Each entity has a unique identifier and a variety of attributes associated with it.
2. Relationships
Relationships define how different entities are connected and interact with each other in the Knowledge Graph. These relationships help search engines understand the associations and dependencies between entities.
3. Attributes
Attributes are the specific properties or characteristics of an entity. For example, for a person entity, attributes may include their name, date of birth, occupation, and notable accomplishments.
Understanding the components of the Knowledge Graph, such as entities, relationships, and attributes, helps us comprehend how search engines use this technology to enhance search results. The examples provided demonstrate how the Knowledge Graph is incorporated into search engine results pages, offering users a more comprehensive and informative search experience.
Types of Structured Data
1. Microdata
Microdata uses HTML tags to mark up specific pieces of information on a web page. It provides a way to label information such as names, dates, and prices, making it easier for search engines to identify and display relevant information in search results.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Book Example with Microdata</title>
</head>
<body>
<div itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/Book">
<h1 itemprop="name">The Catcher in the Rye</h1>
<div itemprop="author" itemscope itemtype="http://schema.org/Person">
<span itemprop="name">J.D. Salinger</span>
</div>
<span itemprop="publisher">Little, Brown and Company</span>,
<span itemprop="datePublished">1951</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>2. RDFa
RDFa stands for Resource Description Framework in Attributes. It adds structured data to HTML using attribute-level annotations. Similar to microdata, RDFa helps search engines better understand the content of a web page and display relevant information in search results.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Book Example with RDFa</title>
</head>
<body>
<div vocab="http://schema.org/" typeof="Book">
<h1 property="name">The Catcher in the Rye</h1>
<div property="author" typeof="Person">
<span property="name">J.D. Salinger</span>
</div>
<span property="publisher">Little, Brown and Company</span>,
<span property="datePublished">1951</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>3. JSON-LD
JSON-LD, or JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data, is a popular format for presenting structured data. It uses JavaScript notation to include structured data on a web page. JSON-LD is a preferred method by Google, as it allows for easy integration and maintenance of structured data.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Book Example with JSON-LD</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "http://schema.org/",
"@type": "Book",
"name": "The Catcher in the Rye",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "J.D. Salinger"
},
"publisher": "Little, Brown and Company",
"datePublished": "1951"
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The Catcher in the Rye</h1>
<p>Author: J.D. Salinger</p>
<p>Publisher: Little, Brown and Company</p>
<p>Date Published: 1951</p>
</body>
</html>How Search Engines Use Structured Data
Google uses structured data to enhance search results by displaying additional information alongside traditional blue links. This additional information, known as rich snippets, can include images, ratings, prices, and other relevant details. Rich snippets make search results more visually appealing and can increase click-through rates.
Structured Data Markup and Google’s Rich Results
Google uses structured data markup to generate rich results, which are enhanced search results that provide more information about a web page’s content. By adding structured data markup to your web pages, you increase the chances of your website appearing in rich results, which can lead to higher visibility and more traffic.
To implement structured data markup on your website, you can use the Structured Data Markup Helper provided by Google. This tool guides you through the process of tagging the relevant information on your web page and generates the necessary markup code.
Schema.org – The Vocabulary for Structured Data on the Web

Schema.org is a collaborative project between Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex to create a standard vocabulary for structured data on the web. It provides a comprehensive library of schemas, which define the properties and values for different types of structured data. By using schema.org schemas, you ensure that your structured data is universally understood by search engines.
Implementing structured data on your website using schema.org schemas allows search engines to better understand your content and display more informative search results, increasing the visibility and click-through rates of your web pages.
Understanding and implementing structured data is crucial for improving your website’s visibility in search results. By using the recommended markup formats, such as microdata, RDFa, and JSON-LD, and adhering to the standards set by schema.org, you can optimize your website for Google’s rich results and increase your chances of ranking on page 1 of Google.
Choosing the Type of Structured Data
When it comes to implementing Structured Data, the first step is to choose the right type for your website. Here are some popular options:
- Article: Use this type for blog posts, news articles, or any content that follows a journalistic format.
- Recipe: If your website features recipes, this type will help search engines present your recipes in a visually appealing manner.
- Event: Use this type if you organize events or have information about upcoming events on your website.
- Product: If your website sells products, using this type will make it easier for search engines to display relevant product information.
- FAQ: If you have a Frequently Asked Questions section on your website, this type will help search engines present the FAQs in a more structured manner.
Identify the Content and Elements to Add Structured Data
Once you have chosen the type of Structured Data, the next step is to identify the specific content and elements that you want to mark up. For example:
- For an Article type, you might want to add the headline, date, author, and a featured image.
- For a Recipe type, you would mark up the recipe name, ingredients, cooking time, and instructions.
- For an Event type, you would specify the event name, date, location, and ticket information.
Implement Structured Data using HTML and Code
To implement Structured Data, you can manually add the required HTML tags to your website’s code. Here’s how you can do it:
- Use the appropriate Schema markup vocabulary for your chosen Structured Data type.
- Add the necessary HTML tags and attributes to enclose the content and elements you want to mark up.
- Test your implementation using Google’s Rich Results Test tool (more on this in the section, “Validate and Test Structured Data using Google’s Rich Results Tool”).
Implement Structured Data using Plugins or CMS Features
If you’re not comfortable with coding or prefer a more user-friendly solution, you can use plugins or CMS features that offer built-in support for Structured Data. Some popular options include:
- Yoast SEO: This WordPress plugin allows you to easily add Structured Data to your website without touching any code.
- Shopify: If you have an online store on the Shopify platform, it provides built-in support for product Structured Data.
- Joomla: This CMS offers extensions like JoomSEF and OSContent that help you implement Structured Data without coding.
Validate and Test Structured Data using Google’s Rich Results Tool
Before deploying Structured Data on your live website, it’s crucial to validate and test it to ensure everything is working correctly. Google’s Rich Results Test tool comes in handy for this purpose:
- Enter the URL of the page you want to test or paste the code snippet.
- The tool will analyze the Structured Data and inform you of any errors or warnings.
- Make the necessary revisions and retest until the tool shows no errors.
Adding Structured Data to your website not only helps search engines understand your content better but also increases the chances of your website appearing in the coveted Knowledge Graph and getting better visibility in search results. Drive organic traffic to your site and dominate SERPs. So take the time to implement it correctly and reap the rewards!